Knee Muscle Anatomy Mri - Mri Anatomy Of Knee Dr Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar - The knee joins the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia).
Knee Muscle Anatomy Mri - Mri Anatomy Of Knee Dr Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar - The knee joins the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia).. Wraps around femur anteromedially (front and inside part of the thigh). Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows (>>) on both side of the image to move the images. The images may also help physicians to distinguish normal, healthy tissues from dead tissues(2). They are attached to the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and fibula (calf bone) by fibrous tissues called ligaments. Thigh muscles are responsible for allowing normal gait and proper lower extremity function(1).
In conclusion, we describe the normal mri anatomy of the distal biceps femoris and the relationship of this muscle with the common peroneal nerve. These muscles work in groups to flex, extend and stabilize the knee joint. Please email baodo at stanford.edu They are attached to the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and fibula (calf bone) by fibrous tissues called ligaments. The femur, tibia and patella.the arrangement of the bones in the knee joint, along with its many ligaments, provide it with the arthrokinematics that allows for great stability, combined with great mobility.being arguably the most stressed and exposed joint of the body, the knee joint is predisposed to various.
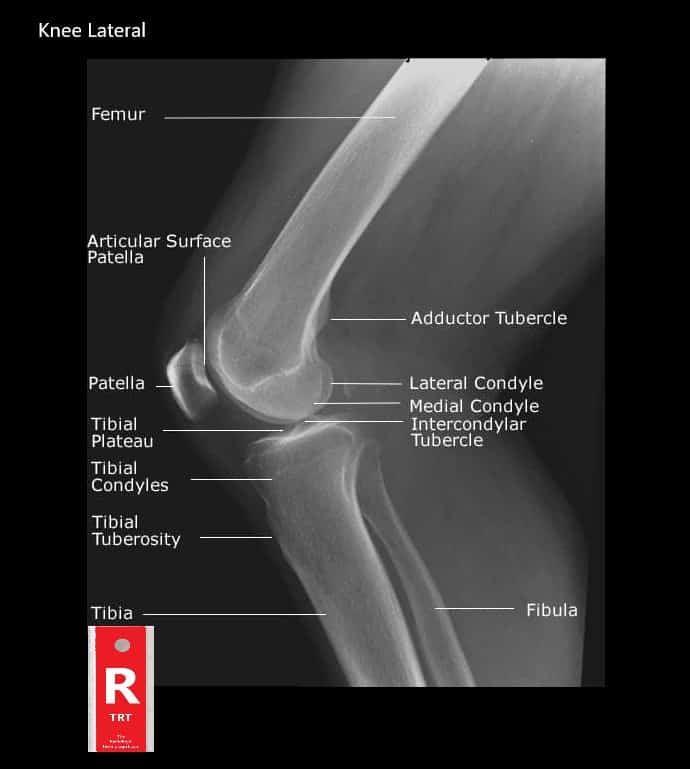
These motions of the knee allow the body to perform such important movements as walking, running, kicking, and jumping.
Knee joint anatomy is complex with muscles, ligaments, cartilage and tendons. The images may also help physicians to distinguish normal, healthy tissues from dead tissues(2). Anatomy of the knee is complex, through the use of magnetic resonance imaging, clinicians can diagnose ligament and meniscal injuries along with identifying cartilage defects, bone. These muscles work in groups to flex, extend and stabilize the knee joint. Anatomy of peritoneum and mesentery. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri scan): They are attached to the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and fibula (calf bone) by fibrous tissues called ligaments. The smaller bone that runs alongside the tibia (fibula) and the kneecap (patella) are the other bones that make the knee joint. An exercise program can strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, increasing the knee's stability. The test can also provide detailed images of various sections of the knee, such as bones, cartilage, tendons, muscles, blood vessels, and ligaments. Knee springerlink / radiology imaging medical anatomy human anatomy and physiology anatomy study. This mri knee sagittal cross sectional anatomy tool is absolutely free to use. Prescribe sagittal plane off axial images with line parallel to bony glenoid.
Stanford msk mri atlas, radlex Each anatomical structure was labeled interactively. T2w axial fat sat 1. They are attached to the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and fibula (calf bone) by fibrous tissues called ligaments. The knee joint is a complex joint that connects three bones;

Please email baodo at stanford.edu
Each anatomical structure was labeled interactively. The knee joins the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). Louis, usa and the rijnland hospital in leiderdorp, the netherlands Knee springerlink / radiology imaging medical anatomy human anatomy and physiology anatomy study. Routine ankle magnetic resonance imaging (mri) tests involve taking images of the foot and ankle in the axial, coronal, and sagittal planes parallel to the tabletop(2). Injuries such as anterior cruciate ligament, meniscus and rotator cuff tears are all easily diagnosed when there is a firm understanding and knowledge of human anatomy. The test can also provide detailed images of various sections of the knee, such as bones, cartilage, tendons, muscles, blood vessels, and ligaments. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) interpretation of the knee is often a daunting challenge to the student or physician in training. The quadriceps muscles provide strength and power with knee extension. The common peroneal nerve typically courses downward within abundant fat posterior to the short head of the biceps femoris muscle and superficial to the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle, but. David rubin and robin smithuis. Knee muscle anatomy mri : Anatomical structures of the lower limb (hip, thigh, knee, leg, ankle and foot) and specific regions (compartment of the lower limb) are visible on dynamic labeled images.
In conclusion, we describe the normal mri anatomy of the distal biceps femoris and the relationship of this muscle with the common peroneal nerve. Home » unlabelled » knee muscle anatomy mri : Popliteus muscle popliteus tendon posterior horn of lateral meniscus head of fibula anterior horn of lateral meniscus lateral femoral condyle 58. The knee joint is a complex joint that connects three bones; Coronal images are perpendicular to the long axis of the metatarsals.
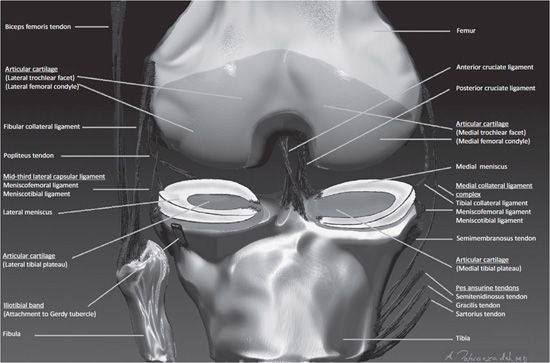
The images may also help physicians to distinguish normal, healthy tissues from dead tissues(2).
In conclusion, we describe the normal mri anatomy of the distal biceps femoris and the relationship of this muscle with the common peroneal nerve. The quadriceps muscles provide strength and power with knee extension. Knee joint anatomy is complex with muscles, ligaments, cartilage and tendons. Mri knee joint anatomy 1. Thigh magnetic resonance imaging the thigh has some of the body's largest muscles. An exercise program can strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, increasing the knee's stability. Medical images from an mri allow medical professionals to distinguish body tissues, including the meniscus (shock absorbers in the knee), cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. T2w axial fat sat 1. Home » unlabelled » knee muscle anatomy mri : Anatomical structures of the lower limb (hip, thigh, knee, leg, ankle and foot) and specific regions (compartment of the lower limb) are visible on dynamic labeled images. Thigh muscles are responsible for allowing normal gait and proper lower extremity function(1). Knee muscle anatomy mri : Anatomy of the knee is complex, through the use of magnetic resonance imaging, clinicians can diagnose ligament and meniscal injuries along with identifying cartilage defects, bone.

Komentar
Posting Komentar